Chronic intermittent hypoxia reveals role of the Postinspiratory Complex in the mediation of normal swallow production
Figures
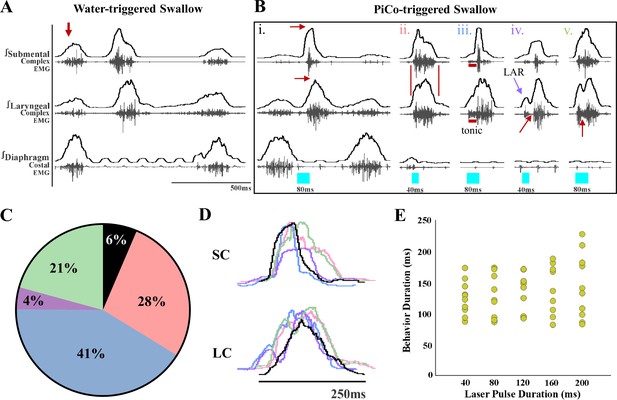
Optogenetic stimulation of postinspiratory complex (PiCo)-specific ChATcre:Vglut2FlpO:ChR2 neurons triggers variable swallow motor patterns in mice exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH).
(A) Representative trace of water-triggered swallow. (B) Representative traces of PiCo-triggered swallows: (Bi) ‘Classic’ swallow with the preserved rostrocaudal sequence shown in the red arrows. (Bii) ‘Non-classic’ swallow with similar onset, offset, and loss of sequence in submental and laryngeal complexes. (Biii) ‘Tonic’ pre-swallow activity with preserved rostrocaudal sequence and low tonic submental and laryngeal activity during the laser pulse, converging into a swallow. (Biv) ‘Laryngeal adductor reflex’ (LAR) (blue arrow) followed by a swallow. There is a period of quiescent activity between the LAR and swallow (red arrow). (Bv) ‘Non-LAR’ followed by a swallow. There is an absence of quiescent activity between the laryngeal activity and the swallow (red arrow). (C) Percentage of all PiCo-triggered swallows (816 total swallows) in ChATcre:Vglut2FlpO:ChR2 mice. Black is classic, pink is non-classic, blue is tonic, purple is LAR, and green is non-LAR. (D) Representative traces of submental complex (SC) and laryngeal complex (LC) from the swallows in (B) with color coding the same as (C). (E) Scatter plot of behavior duration versus laser pulse duration for swallow in ChATcre:Vglut2FlpO:ChR2 mice (N = 11). Each gold dot represents the average duration per mouse.
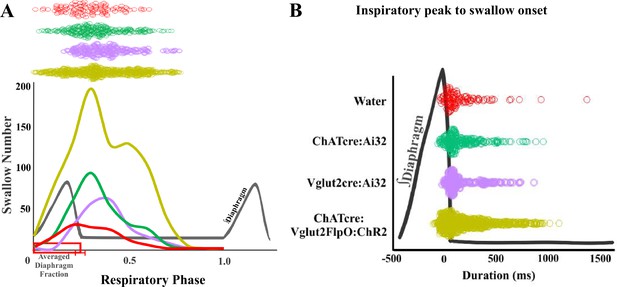
No significant differences in swallow-breathing characteristics between water-triggered swallows and postinspiratory complex (PiCo)-triggered swallows in mice exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH).
(A) Line graph of swallow frequency in relation to the onset of inspiration for water swallows (red), ChATcre:Ai32 (green), Vglut2cre:Ai32 (purple), and ChATcre:Vglut2FlpO:ChR2 (gold). (B) Dot plot of each swallow in relation to the inspiratory peak. Data for each genetic type is located in Supplementary file 1.
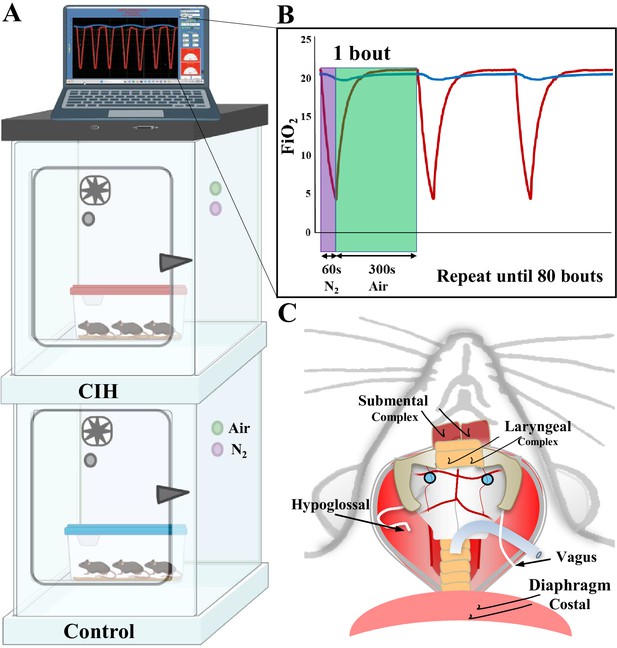
Chronic intermittent experimental protocol.
(A) Equipment setup for control and chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) protocols. Two plexiglass chambers supplied with a fan, oxygen sensor, and valves for compressed air and nitrogen. The top chamber serves as the CIH chamber where the oxygen level is automatically controlled by the Oxycycler computer software on top of the chambers. The bottom chamber serves as the control chamber where only air flows through the chamber and the oxygen level is kept at 21% O2. The mice are kept in their home cage and placed in either chamber for 21 d. (B) In the CIH chamber, nitrogen (N2, purple dot) flows into the chamber for 60 s, or until the O2 level reaches 5%. In the event the O2 level reaches 5% before 60 s, no gas flows into the chamber. After 60 s, compress air (green dot) flows into the chamber for 5 min. These 6 min create one bout and is repeated 80 times a day. (C) Graphical depiction of all muscles: submental complex, laryngeal complex and diaphragm; and nerves: hypoglossal and vagus, recorded to measure swallow and breathing activity. The blue circles depict optrode placement over postinspiratory complex (PiCo).
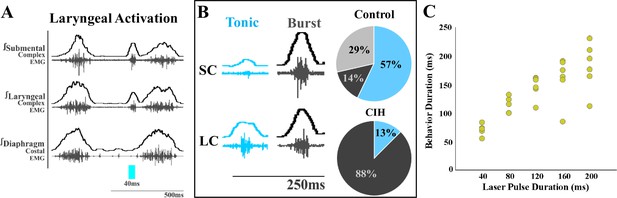
Optogenetic stimulation of postinspiratory complex (PiCo)-specific ChATcre:Vglut2FlpO:ChR2 neurons stimulates submental complex burst during laryngeal activation in mice exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH).
(A) Representative traces of PiCo-stimulated laryngeal activation with burst pattern submental complex activity. (B) Representative traces of laryngeal activation-related submental complex activity patterns, tonic and burst, and percent of each mouse with the corresponding pattern in control and CIH mice. In control ChATcre:Vglut2FlpO:ChR2 mice, four mice had tonic submental complex activity, one burst activity, and two no submental activity (Huff et al., 2023). In CIH-exposed, one mouse had tonic activity and seven burst submental activity. (C) Scatter plot of behavior duration versus laser pulse duration for laryngeal in ChATcre:Vglut2FlpO:ChR2 CIH-exposed mice. Each gold dot represents the average duration per mouse.
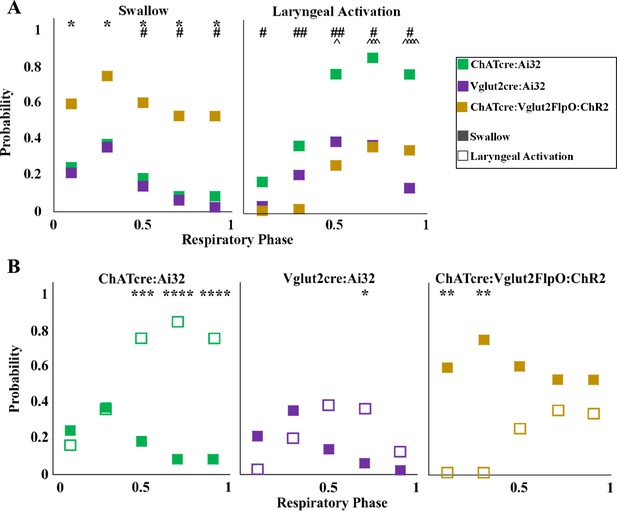
Optogenetic stimulation of postinspiratory complex (PiCo) neurons in mice exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) regulates swallow and laryngeal activation in a phase-specific manner.
(A) Scatter plot of the probability of triggering a swallow (left) or laryngeal activation (right) across the respiratory phase (0 start of inspiration, 1 start of next inspiration) in ChATcre:Ai32 mice (green) Vglut2cre:Ai32 mice (purple), and ChATcre:Vglut2FlpO:ChR2 mice exposed to CIH (gold). * indicates significant difference in probability between Vglut2cre:Ai32 and ChATcre:Vglut2FlpO:ChR2, # indicates significant difference in probability between ChATcre:Ai32 and ChATcre:Vglut2FlpO:ChR2, and ^ indicates significant difference in probability between ChATcre:Ai32 and Vglut2cre:Ai32. (B) Scatter plot of the probability of triggering a swallow (closed square) versus laryngeal activation (open square) in all three genetic types exposed to CIH.

Postinspiratory complex (PiCo)-triggered swallows reset the respiratory rhythm, while non-swallows have minimal effect, a concept not altered by chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH).
Respiratory phase shifts plots were divided into two groups: swallow, PiCo activation that triggered a swallow, or non-swallow, PiCo activation that resulted in laryngeal activation or no motor response. (A) Individual responses in ChATcre:Vglut2FlpO:ChR2 (gold), ChATcre:Ai32 (green), and Vglut2cre:Ai32 (purple) mice exposed to CIH and (B) line of best fit from the above graphs.
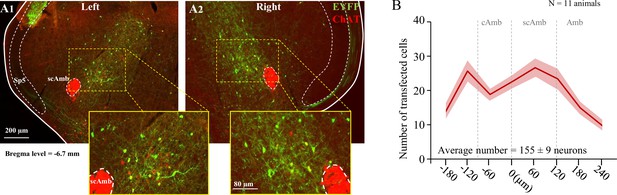
Transfection of cholinergic/glutamatergic neurons in postinspiratory complex (PiCo) in ChATcre:Vglut2FlpO:ChR2 chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH)-exposed mice.
(A) Transverse hemisection through Bregma level (–6.7 mm) of the transfected neurons into PiCo bilaterally, left (A1) and right (A2), with the pAAV-hSyn Con/Fon hChR2(H134R)-EYFP vector. (B) Rostrocaudal distribution of the total number of transfected neurons counted 1:2 series of 25 µm sections into PiCo of 11 animals with an average of 155 ± 9 SEM neurons. Amb, nucleus ambiguus; cAmb, nucleus ambiguus pars compacta; scAmb, nucleus ambiguus pars semi-compacta.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Means, standard deviations (SD), p-values, t-statistic (t), degrees of freedom (df), from a paired t-test; and the direction of change for swallow-related parameters when evoked by water (water swallows) and optogenetic stimulation of PiCo in (A) ChATcre:Ai32, (B) Vglut2cre:Ai32, and (C) ChATcre:Vglut2FlpO:ChR2 mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92175/elife-92175-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Means, standard deviations (SD), p-values, F-value, t-statistic (t), degrees of freedom (df), from an unpaired t-test; and the direction of change for swallow-related parameters between male and female mice during water swallows and PiCo-stimulated swallows in ChATcre:Ai32 mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92175/elife-92175-supp2-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Means, standard deviations (SD), p-values, F-value, t-statistic (t), degrees of freedom (df), from an unpaired t-test; and the direction of change for swallow-related parameters between male and female mice during water swallows and PiCo-stimulated swallows in Vglut2cre:Ai32 mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92175/elife-92175-supp3-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Means, standard deviations (SD), p-values, F-value, t-statistic (t), degrees of freedom (df), from an unpaired t-test; and the direction of change for swallow-related parameters between male and female mice during water swallows and PiCo-stimulated swallows in ChATcre:Vglut2FlpO:ChR2 mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92175/elife-92175-supp4-v2.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92175/elife-92175-mdarchecklist1-v2.docx





