Human multiethnic radiogenomics reveals low-abundancy microRNA signature in plasma-derived extracellular vesicles for early diagnosis and molecular subtyping of pancreatic cancer
Figures
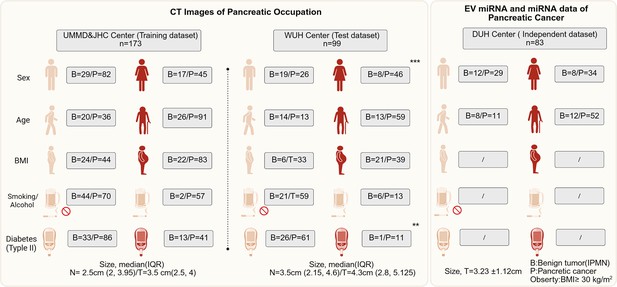
The baseline information of clinical parameters of patients enrolled from four centers in this multicenter trial.
The intergroup comparisons were performed using the chi-square test.The * means p less than 0.05, ** means p less than 0.01, and ***means p less than 0.001.
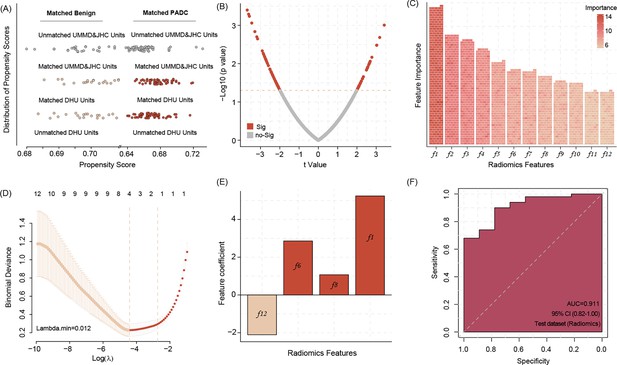
Propensity score matching (PSM) allows matching data of benign pancreas lesions and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patients from DUH to UMMD and JHC patients according to the age factor, all of DUH patients successfully matched similar patients (A).
The different radiomic features between the benign lesions and PDAC patients’ computed tomography (CT) images (B) Twelve most important radiomic features differentiating between the benign pancreatic lesion and PDAC patients’ CT images identified by the Boruta algorithms (C) Four radiomic features were selected by Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression to build model signature (D, E). Applying the four radiomic features related signature in image analysis shows high accuracy in predicting the PDAC manifestation in the WUH test dataset (F).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Important radiomic features.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/103737/elife-103737-fig2-data1-v1.docx
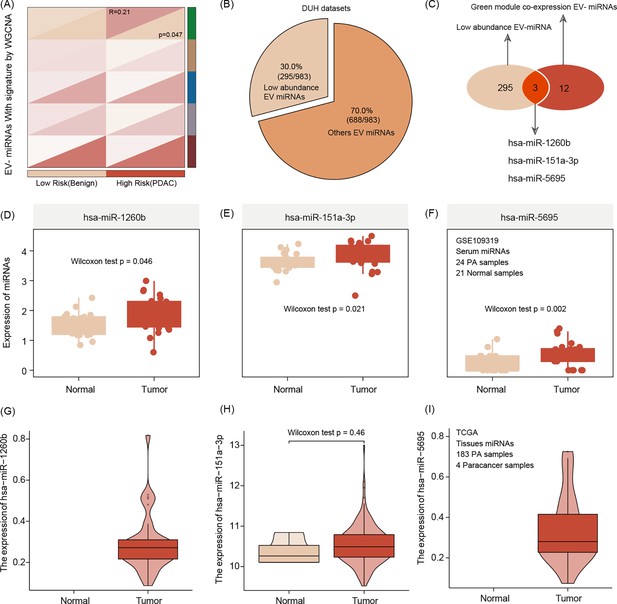
Extracellular vesicle (EV) miRNA presenting the risk group stratification based on radiomics signature by weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) featuring green mode discovering our key module for further analysis (r = 0.21, p = 0.047).(A).
The number of low-abundance miRNAs in the entire EVseq dataset cohort is n = 295 (B) Out of those low-abundance miRNAs, n = 12 present matching candidates differentially expressed in high-risk group patients. Alignment to our radiomics feature parameters identified three core miRNAs (hsa-miR-1260b, hsa-miR-151a-3p, and hsa-miR-5695) (C) The three key miRNAs show significantly different expression levels in tumor conditions, both for serum (D–F) and tissue (G–I) The Wilcoxon test was used to compare differences between two groups.
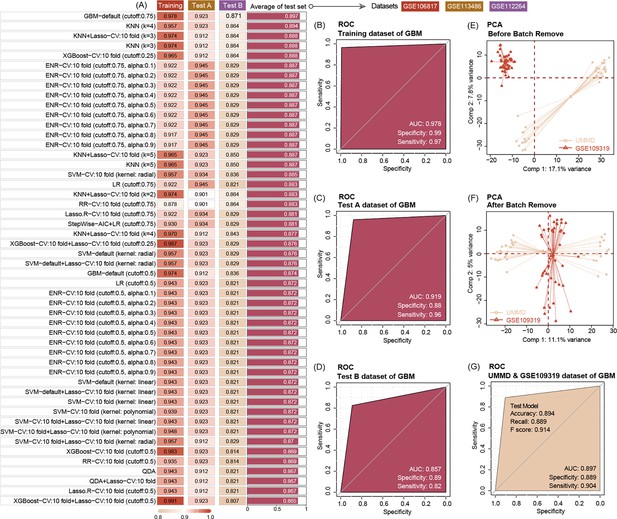
Ten machine-learning algorithms demonstrate that three key miRNAs show a high accuracy to diagnose pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) in early stage, no matter in training or test datasets.
The best machine-learning algorithms are GBM (cut-off: 0.75) (A). Three miRNAs’ prediction ability of the training dataset (GSE10106817) in the GBM model is 0.978 (B). Three miRNAs’ prediction ability of the test dataset (GSE113486 and GSE112264) in the GBM model is 0.919 and 0.857, respectively (C, D). Data distribution before removal of batch effect of our center data and GSE109319 dataset (E). Data distribution after removing batch effect of our center and GSE109319 dataset (F). Three extracellular vesicle (EV) miRNAs’ prediction ability to identify cancer of our center data and GSE109319 in GBM model is 0.897 (G).
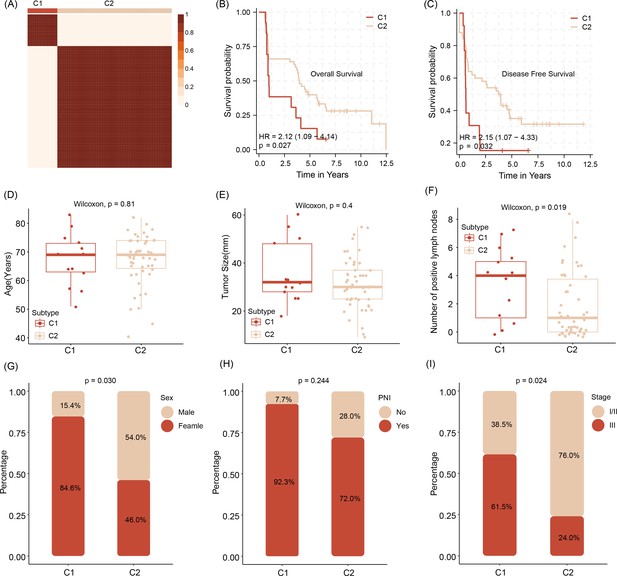
Stratification of abundancy levels of shared mRNAs by non-negative matrix factorization method allows the clustering of patients into two subtypes (C1 and C2) (A).
Patients of the C1 with a poor outcome in OS and DFS (B, C). C1 subtype patients are characterized by older age and bigger average tumor size, higher number of tumor cell positive lymph nodes as compared to C2 patients (D–F). C1 patients are predominantly female, have tumors with pathological classification marks of perineural invasion/ PNI and advanced tumor stage (G–I).Survival analysis was performed using the log-rank test. Differences in continuous variables between groups were assessed using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test, while differences in categorical variables were analyzed using the chi-square test.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Shared targets of three extracellular vesicle (EV) miRNAs.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/103737/elife-103737-fig5-data1-v1.docx
-
Figure 5—source data 2
NMF rank survey of shared targets of three extracellular vesicle (EV) miRNAs.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/103737/elife-103737-fig5-data2-v1.pdf
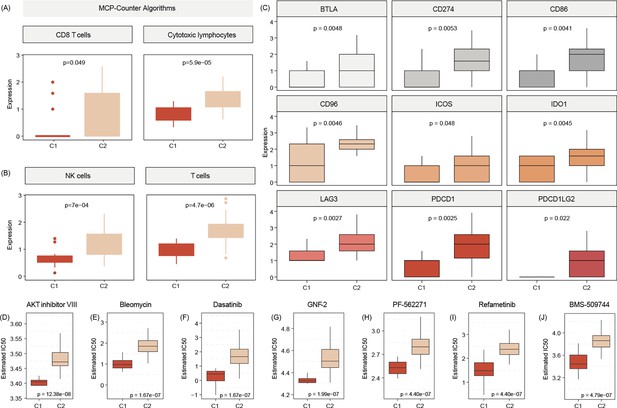
C2 subtype is positively associated with elevated levels of transcripts regulating gene pathways encoding for CD8 T cells, cytotoxic lymphocytes, and NK cells (A, B).
Commonly known immune checkpoints are also higher expressed in C2 subtypes (C) Aligning in vitro drug sensitivity and expression data from the GDSC database to subtype signature predicts that tumors of C1 patients might be more sensitive to AKT INHIBITOR VIII, Bleomycin, Dasatinib, GNF-2, PF-562271, Refametinib, ans BMS-509744 as C2 subtypes (D-J).The Wilcoxon test was used to compare differences between two groups.
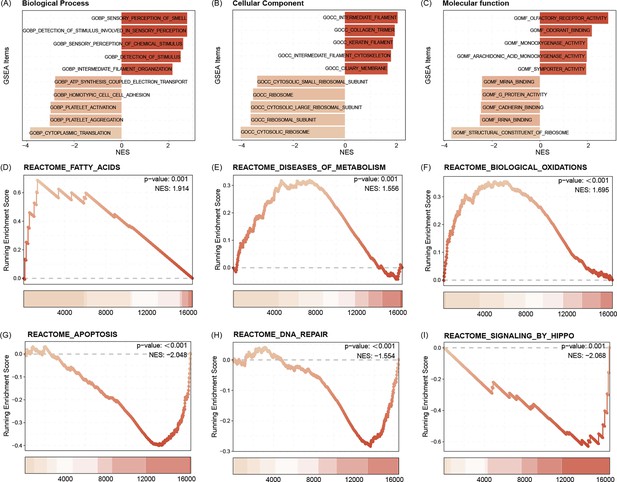
GO functional enrichment analysis indicated that the C1 subtype is enriched for intermediate filament organization, CC ribosome, as well as MF symporter activity (A–C).
Pathway enrichment analysis showed that the C1 subtype was activated with the Reactome fatty acids, Reactome diseases of metabolism, as well as Reactome biological oxidations pathways, and may be inhibited with Reactome apoptosis, Reactome DNA repair, and Reactome signaling by Hippo pathways (D–I).